2023-09-14 | Andrea Folger | 3 min read
Spotify Model in a nutshell
If I ask you if you have ever heard of Spotify, I'm sure your answer will be "Yeah sure, who doesn't know Spotify?". Spotify is known to most of us, because we use the audio streaming service to listen to music, podcasts or audio books. Spotify accompanies us as an app on our mobile phones in our free time, on the way to work, in the waiting room at the doctor's office and in many more places.
But if I ask you now, have you ever heard of the Spotify model? What's your answer then? I'm guessing something along the lines of "Phew, heard it before possibly, but what that is exactly, no idea..." - Never mind, because in this blog post I'll explain the Spotify model to you and how it can help organizations to scale agilely.
Spotify started as a startup in Sweden in 2006. The development teams relied on agile methodologies like the Scrum framework. Over time, the organization grew and they had to face new challenges, creating a new organizational model, the Spotify model, to enable agile ways of working not only at a team level but across the entire organization. The focus here was very much on culture and network. The Spotify model is not to be understood as a framework, but it is an example of agile scaling.
When we look at the Spotify model in detail, we use the following terms: squads, tribes, chapters, and guilds. I'll tell you what's behind the names and how each is composed in the following section.
Squads
Let's start with squads. These are comparable to a Scrum team and form the basis of the Spotify model. Squads are self-organized agile teams that include all the resources it takes to develop a product or service from start to finish. Of course, each of these teams also has a product owner who is responsible for the backlog and prioritization. In addition, each squad has an agile coach to provide methodological support to the team and organize events such as retrospective or planning.
Tribes
A tribe comprises several squads that work together on a product or service. There is a so-called tribe lead who ensures that the squads can work together in the best possible way. There are regular meetings where the squads can exchange ideas and present their work so that everyone is up to date.
Chapters
A chapter includes employees with the same expertise. These are distributed among the different squads within a tribe. Chapters also have a chapter lead, who organizes regular meetings to enable an exchange among each other.
Guilds
Guilds are gatherings of people with the same skills or interests from different tribes. The so-called guild coordinator takes care that meetings take place where the members of the guilds can exchange information. This has a great advantage for the improvement of the organization.
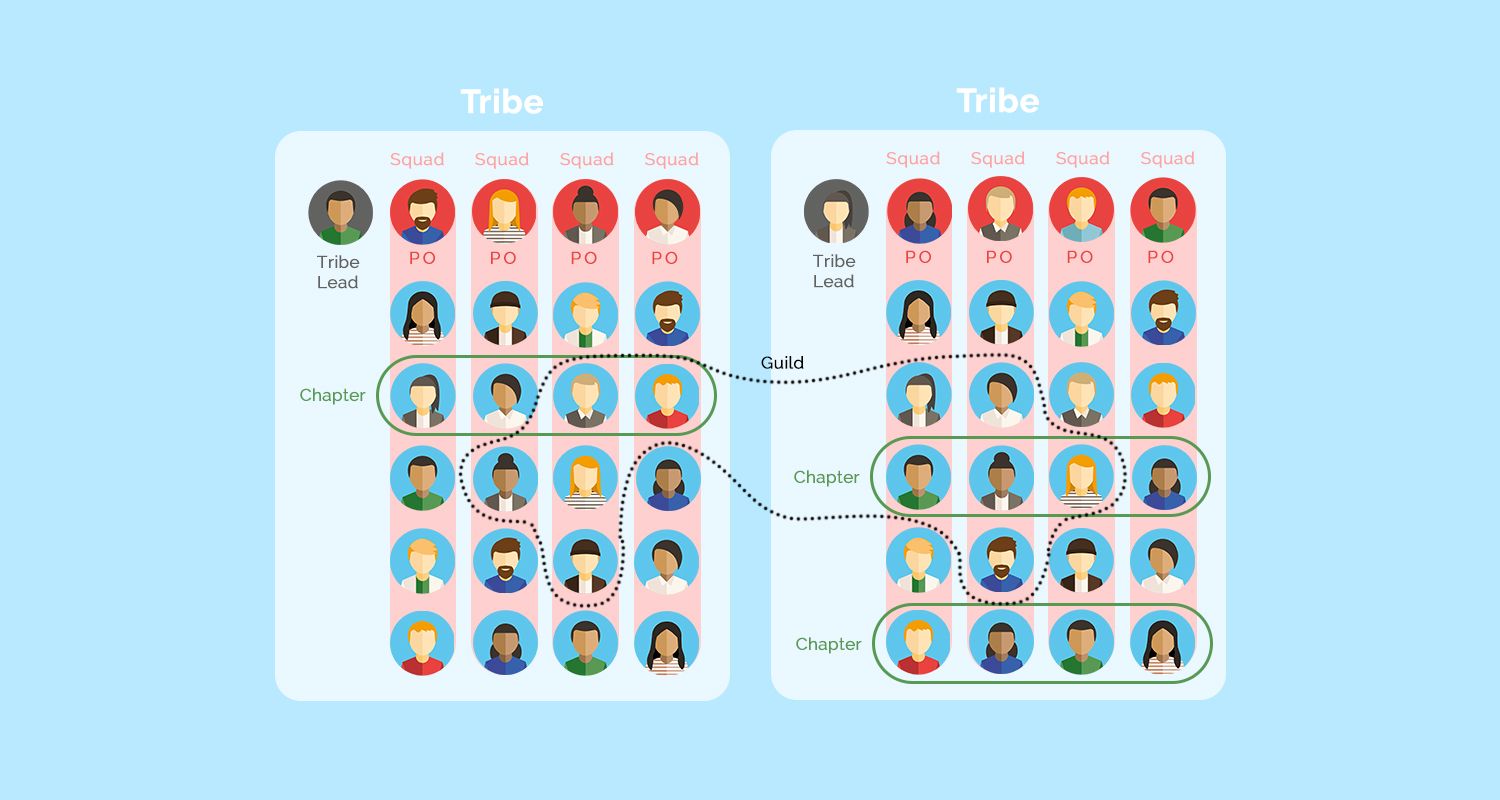
To recap: Under the Spotify model, an organization is divided into tribes, which are responsible for developing a product or service. Within a tribe, members with different expertise (squads) are brought together to independently develop a product or service. In addition, members with the same expertise are brought together, both within a tribe (chapters) and across tribes (guilds) for experience sharing and further development.
Unlike what we know from frameworks such as Scrum, there are no practices that must be followed or mandatory meetings that must be held. Squads self-organize how they best get their work done. This can happen through the use of the Scrum framework, Kanban, or other methods.
Likewise, chapters and guilds determine for themselves how they want to best organize their collaboration.
Now you can confidently answer yes to the question if you are familiar with the Spotify model.



